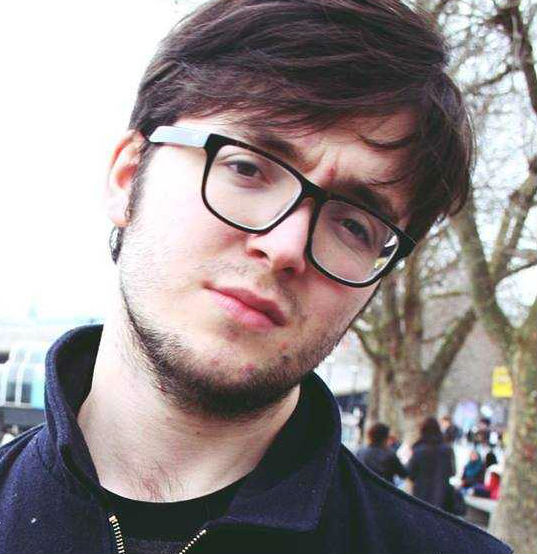



You are unlikely to see a more important documentary made all year than Welcome to Chechnya. A work of investigative journalism depicting an undercover LGBTQ network helping gay men and woman escape from the barbarous Chechen regime, it is a breathtaking, invigorating and necessary work. We sat down with its director David France during the Berlinale, where it played in the Panorama Section, to discuss the making of the film, his thoughts about the region and whether the film may even be released in Russia itself.
Redmond Bacon –How did you gain access to Chechnya? This is a closed-off area…
David France – We had a cover story of why I was in Chechnya. It’s not a place that Americans go to visit or anybody goes to visit. But the World Cup was there so I posed as a wealthy American football fan, especially enamoured with the Egyptian team who had stayed in Chechnya. I hired these people to take me on a tour and they agreed because I was throwing money around. That was our story. I had to study up on football…
RB – What is the atmosphere in Chechnya like?
DF – I had never been in a place that is so closed. I felt watched and studied. There’s something in the air that I’ve never experienced before. I don’t even know how to describe it. I have done war reporting in Central American, Lebanon, Occupied Territories, Western Africa, but I never felt the kind of peril that you felt when you were there even though you didn’t really see it. There were no goons with guns and no military infrastructure in front of you, but you felt it anyway.
RB – What filmmaking techniques did you have to use?
DF – The two women who met with Anya were wearing hijabs. One of them was my DP, and she was shooting with a go-pro. I was across the restaurant with a cellphone, taking selfies or appearing to take selfies. It was guerrilla filmmaking.
RB – What kind of emotions did you feel? Did it feel dangerous?
DF – Not really. We had prepared very well with our security team. But we were detained briefly as we were leaving. That’s the scene in the film where they are reaching for passports. They were reaching for my passport and I had my cellphone between my legs and I was shooting that way. And when they called me out the car I just dropped the phone and walked out. I had a second cellphone that had all of my football fan tourism on it and they were shocked by the story we told them about me needing to come and see the Egyptian football in Chechnya. Eventually they were like: “this guy is way too crazy”. We were heading in the right direction out of the region anyway, so they just threw us back in the car.
RB – Can you talk about the danger for your documentary subjects? For them, this is life or death...
DF – It was especially dangerous for them. That’s why they wanted me there. The video would present an alibi if needed. “What are they doing there? Are they kidnapping this girl? Who are they? Is she consenting?” All of these questions would be disproved by whatever video we were shooting. In a way we were functioning as a failsafe for the activists and the work they were doing.
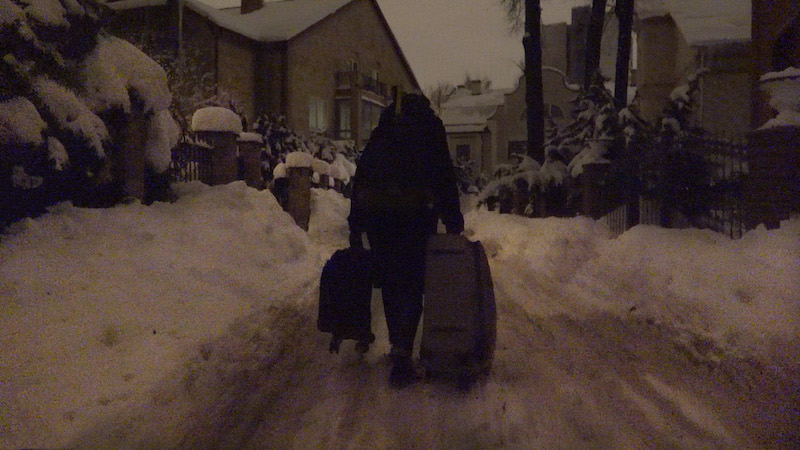

RB – How did you initially establish contact with the LGBT network?
DF – I had read an interview with Olga Baranova, who is running the main shelter in Moscow. She had spoken publicly about her work. I was introduced to her and proposed that we make a documentary. She was interested at first, but there were the questions of security and protecting the identities of people within the shelter. We worked that all out quickly. Within three days I was there shooting.
RB – How did you come up with the idea to obscure their faces digitally while still allowing the audience to see their emotions? What was the rationale behind it?
DF – I had to make the argument to people who were on the run that we needed to see their faces in order to generate empathy. I needed to know what it was like to be them, to have been tortured so terribly, to have barely escaped, to be so dislocated from everyone, even your family, and to know that even your family has joined the hunt for you.
I promised everybody I would disguise them in some way although I didn’t know how yet. And yet they still agreed to let me do this. I had in my release form a question asking if they needed to be covered, or if they needed their voices to be disguised. And they would check those boxes and everybody on the run checked those boxes. I promised that I would return to them with my solution for their approval. I think they realised it was going to be a breakthrough film in this respect.
Once we began the work of research and development to find ways to cover them we began to worry very seriously that we had a movie that we would never be able to release.
Thankfully it worked and it’s been recognised as major new tool for documentary filmmakers. It gives back the power to people to tell their own stories. It gives them back their humanity.
RB – Did you worry that the film may have blown the network’s cover?
DF – They had a trade-off that they were weighing and that was their need to get the world to pay attention to what they’re doing. This was also the reason for the activists to appear with their real faces. Due to the increasing physical risk to them and to their safety, they believed that their notoriety from this film will add to their level of protection. David Isteev, for example, expects to do his work in some way. Of course, he’s not going to travel in and out of Chechnya after the film comes out. But he does believe that after passing that torch to others, he will be able to continue living the life he had before.
RB – What can Vladimir Putin do to successfully intervene in Chechnya? The region is volatile, and known for its two wars with Russia…
DF – Putin could tell Ramzan Kadyrov to stop it and Kadyrov could stop it just like that. Why isn’t he telling him? Because I believe that what’s happening in Chechnya is the extension of Putin’s policies for the last ten, fifteen years.
He has been systematically rolling back a cultural acceptance of the LGBT community in Russia. He did it by passing only one law. And that’s what they call the anti-gay propaganda law. This law makes it illegal to say anything in the presence of a minor that might be construed as suggesting the normalcy of LGBT folks.
It is legal to be gay in Russia. There are also no laws against gay sex in Russia, but there are no protections either. But Putin’s campaign in the last fifteen years is to create an appetite for traditional values and to rebuild the role of the Church in society after the collapse of communism. What he has done is weaponised homophobia to consolidate his power. And the logical extension of that is what’s happening in Chechnya, Dagestan, North Ossetia, and numerous other republics in the South and creeping throughout Russia. We’ve seen other explosions of extreme anti-queer violence in Russia.
What shocked me the most is the fact that I didn’t think that homophobia could be weaponised again the way it was in the ’50s, ’60s and ’70s. I thought that would be impossible. In almost every society we have celebrities who are queer, we have politicians running governments who are queer, we have people who are out in the industry and we have people marrying left and right.
But we also currently have the first place and first time since Hitler that a top-down government-sponsored campaign exists to round up LGBTQ people for execution. This hasn’t happened since the 30s.
RB – How challenging was it for you to show these shocking images? What was the reasoning behind them?
DF – It was not a hard decision at all. This is an ongoing crime against humanity that no one is paying attention to.
Without knowing what this persecution looks like, it makes people in the shelter’s journeys dismissible. We wanted to show the grotesqueness of what is happening there and what they are escaping.
RB – Can you talk about the film as a work of investigative journalism. After all, reporting out of Chechnya is scarce.
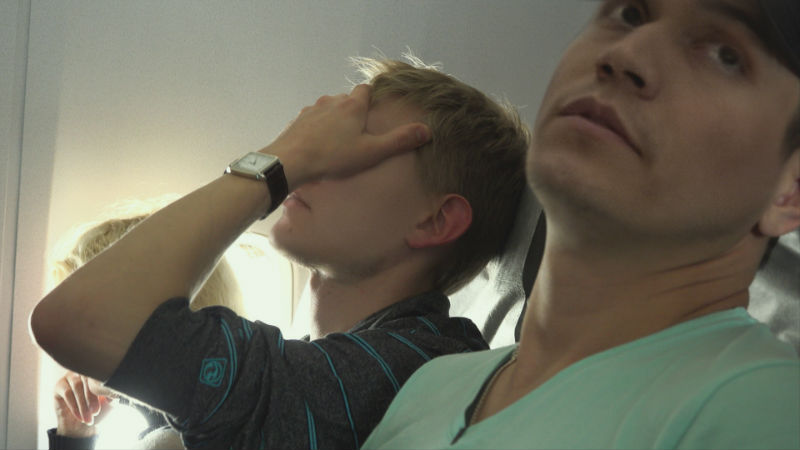

DF – The biggest failure is the failure of the news media. It was a Russian-based independent newspaper, Novaya Gazeta, that broke the story.
They’re the only paper in the world that’s been aggressive about reporting this story. The news cycle throughout the world, and throughout the West especially, has become inexcusably shallow. The economy is not there to continue investigative research and reporting, especially the way we knew it in the past. I’m an investigative journalist myself, I came to filmmaking through that. This film is a piece of investigative work of the sort that newspapers should be doing.
The idea for the movie is to get the story back in the headlines. Then people in the news media can amplify a call for justice from the audience, which will put pressure on governments around the world to bring effective pressure on Putin. Currently the only global leader who has taken him to task on this is Angela Merkel. There’s been nothing out of the United States.
RB – I’m so glad the film also shoots scenes of the refugee Maxim Lapunov and his boyfriend together in the bath and then playing by the beach. Because those are such tender, lovely moments in a film which is mostly very harrowing. Did you feel that you needed to include those love scenes?
DF – I’ve realised very early on that this is a film about love. Not just romantic love, but love in a much larger way. I thought I was making a film about hate but having spent time in the underground network I saw a remarkable expression of love.
I spent so much time with those guys that we, as filmmakers, disappeared. We were able to watch them really without them having any sense of us watching them. But yes, when I crawled into the bathroom they did notice.
RB – Will it play in a few independent cinemas in Moscow or St Petersburg perhaps?
DF – We are in genuine conversations with people at the Moscow Film Festival, and there are additional conversations with another festival in St.Petersburg. We believe that we will be invited there. But in Russia, in order to show a film, it needs a license by the Kremlin.
So whether the Kremlin give a license for this film is certainly an open question. I’m not the one negotiating these deals. We have an agent for foreign sales, who did tell me last night that they are deep in conversation about official commercial distribution in Russia. Will it happen? I don’t know. But I would love to see it happen.
The picture at the top of this article is from David France at the 70th Berlinale, where this interview was conducted, while the other two are from ‘Welcome to Chechnya’
















